Create Task
|
This page explains how to create new tasks and how to add task attributes. It also explains how to add additional properties and how to add new content. Remember to login before creating an new task. ContentsCreate Plain TaskA new root task can be created via the Task Explorer and new subtasks via the
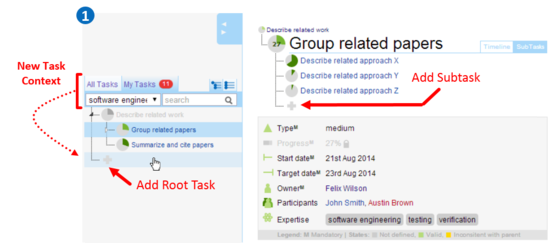
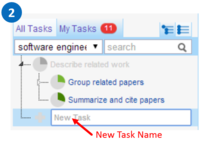
Subtask Explorer. Start by clicking on the plus button, an input
field appears. Type the name of the new task and press enter to confirm. If you have an expertise keyword selected when you create a new
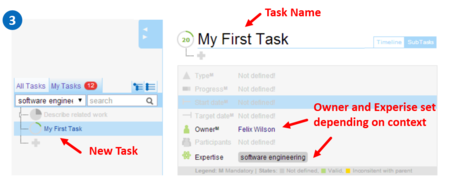
root task, then the system will automatically add that expertise keyword to the task. If the My Tasks tab is selected when you add a new task, the system will set you up as its owner. Add Task AttributesTask attributes are useful to describe tasks. Attributes marked with M are mandatory, because they are
used by the wiki to organize tasks.
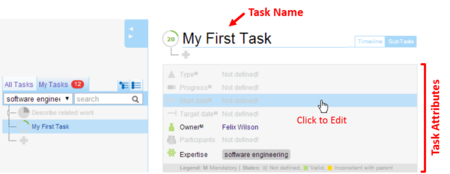
Attributes can be added after a task is created. Click on a attribute row to enable editing.
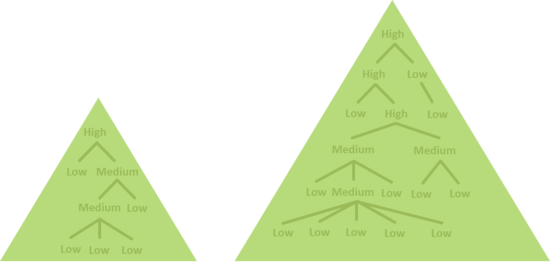
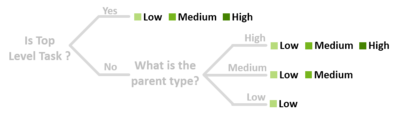
The following sub sections explain all task attributes in more detail. Different attribute states are explained in the last section. Task TypesTask types are used by the system to estimate progress of tasks in different ways. The framework provides three different task types that imply a hierarchical order. We use a different shade of green in the task state icon for every task type. Different task types:
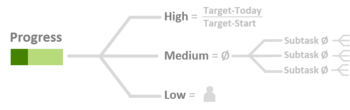
ProgressThe progress of a task indicates how much work has been done as a percentage. The system automatically estimates
progress depending on the task type.
The level of progress of high-level tasks is estimated based on the start date, today's date and
the target date. For medium-level tasks, the progress is estimated by aggregating the progress of their subtasks as an average. The progress of low-level
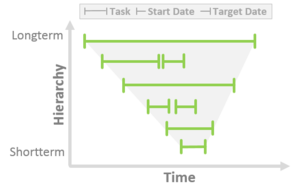
task is always set by the user. Time IntervalThis section summarizes the meta data attributes start date and target date. The time intervals for a task and its subtasks
follow a strictly hierarchical approach. Therefore, the start and target dates of any task must be within the time interval of
the parent task. This leads to a time funnel illustrated on the figure below. If any inconsistency occurs
it will be highlighted in yellow in the Task Status and the Timeline View. OwnerA task owner is responsible for coordinating the activities for a task and overseeing its completion.
Therefore the system expects exactly one owner. All task which are assigned to you as owner are shown in your My Task
tab and on your person page. Persons who have a wiki account are shown in blue and linked to their wiki page.
Persons who do not have an account are shown in red. See participant example. ParticipantEvery task can have many participants. These persons may represent a team or just a working group for the task. Participants
who have a wiki account are shown in blue and linked to their person page.
Persons who do not have an account are shown in red. ExpertiseExpertise keywords are used to indicate the knowledge you might need to accomplish a task. Several expertise keywords can be assigned to a given task. You can easily recognize
expertise keywords in any page by the grey rectangle around them. The task explorer allows to search for tasks with certain expertise keywords. Attributes StatesThe task attribute state is represented with different colors for the attribute icons.
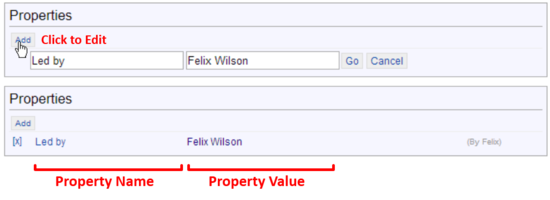
Add Additional AttributesAdding additional custom attributes allow to structure any page content with key value pairs. These additional attributes help to make page content searchable by
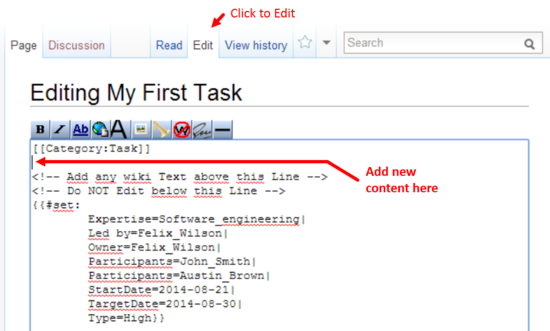
custom properties. You can add a new property by clicking on the add button. Click on the cross to remove a certain property. Add ContentAfter you have added some attributes, you can start adding content to the task page. Click on edit in the top navigation.
The page editor opens and shows the current page content. Note that even empty pages may already have content generated by the system. This is shown on the example below.
It is important that all system-generated content remains untouched. You can add your content between the | Organic Data Science Framework Documentation Contribute as Participant Exploring Tasks Participating on Tasks Person Page Basic Task States Contribute as Owner Create Task Task Alert Organize Tasks Extended Task States |