Difference between revisions of "Main Page"
(→Research Objectives) |
(→Research Objectives) |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
This project seeks to address 4 main objectives: | This project seeks to address 4 main objectives: | ||
| − | * Research Question 1: Understand how human decisions alter nutrient fluxes through lake ecosystems | + | * '''Research Question 1''': Understand how human decisions alter nutrient fluxes through lake ecosystems |
| − | * Research Question 2: Represent the consequences of those fluxes as changes in water quality metrics that are meaningful to people | + | * '''Research Question 2''': Represent the consequences of those fluxes as changes in water quality metrics that are meaningful to people |
| − | * Research Question 3: Determine how those water quality metrics feed back into human decision making | + | * '''Research Question 3''': Determine how those water quality metrics feed back into human decision making |
| − | * Research Question 4: Scale our results and understanding of three focal lake systems to a diverse set of lake systems representative of continental-scale gradients | + | * '''Research Question 4''': Scale our results and understanding of three focal lake systems to a diverse set of lake systems representative of continental-scale gradients |
=== Models === | === Models === | ||
Revision as of 09:46, 10 December 2015
Contents
CNH-L: Linking land-use decision making, water quality, and lake associations to understand human-natural feedbacks in lake catchments
Worldwide, people benefit greatly from the irreplaceable services provided by freshwater lakes, such as drinking water, recreation, and fisheries. However, human activities in lake catchments contribute to eutrophication and the growth of harmful algal blooms that threaten the very waters upon which people depend. This degradation can generate incentives for behavioral change. For example, lake associations can initiate citizen-driven actions to protect and improve water quality, but will this action come in time and focus on the key drivers of water quality.
This project examines the linkages between land-use decision making, fate-transport of nonpoint source pollution to lakes, lake water quality, the effects of water quality on property values, and the community responses that stimulate changes in land uses. In three lake catchments that vary in the intensity of agriculture, forested land and residential development we build the linkages from land use to water quality to identify the key drivers of lake water quality.
The insights from the three focal catchments will inform the understanding of human-natural system dynamics across thousands of lake catchments spanning the northeastern and midwestern U.S. An understanding of the relationships between and lake water quality and land-use policies will be leveraged to support science-based monitoring, advocacy and volunteerism to develop effective programs to protect and enhance lake water quality.
News & Project Events
Check out the Virginia Tech press release about the project at this link.
Our Multidisciplinary Team
This project builds on a strong collaboration among a diverse team of researchers from multiple disciplines and institutions, as well as citizen science groups. Our team's expertise spans the fields of freshwater ecology, environmental and resource economics, hydrology, and social science.
Project Leadership
- Kelly Cobourn (lead PI). Cobourn is an agricultural and resource economist with experience in bio-economic modeling.
- Cayelan Carey (PI). Carey is a freshwater ecologist whose research focuses on understanding the causes and effects of eutrophication in lakes.
- Kevin Boyle (PI). Boyle is an environmental economist who specializes in the development of hedonic models of the impacts of changes in lake water quality on property values.
Co-Principal Investigators
- Chris Duffy, Hydrologist
- Armen Kemanian, Biological Systems Engineer
- Paul Hanson, Aquatic Ecologist
- Michael Sorice, Social Scientist
- Pat Soranno, Landscape Limnologist
- Kathleen Weathers, Biogeochemist
Contributing and Participating
Our extended collaborative includes several scientists and lake associations, including:
- Lars Rudstam, Cornell University
- Jennifer Klug, Fairfield University
- Michael Vanni, Miami University
- Clean Lakes Alliance, Lake Mendota, WI
- Lake Sunapee Protective Association, Lake Sunapee, NH
- Oneida Lake Association, Lake Oneida, NY
Research Objectives
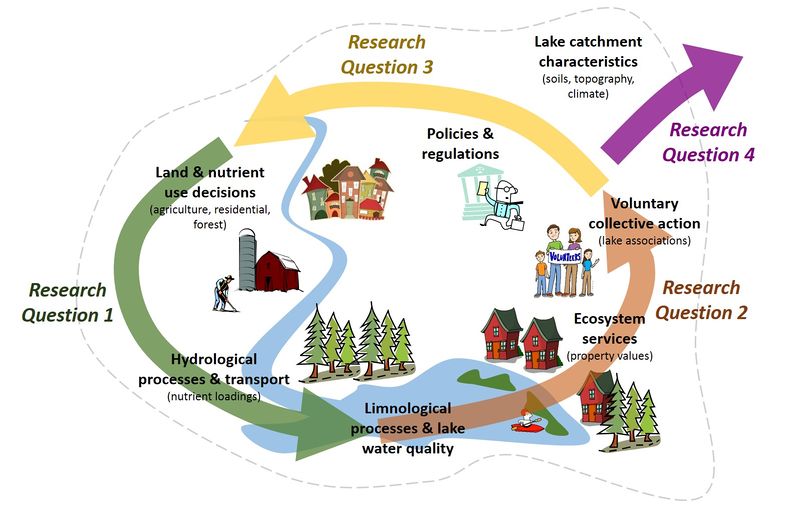
This project seeks to address 4 main objectives:
- Research Question 1: Understand how human decisions alter nutrient fluxes through lake ecosystems
- Research Question 2: Represent the consequences of those fluxes as changes in water quality metrics that are meaningful to people
- Research Question 3: Determine how those water quality metrics feed back into human decision making
- Research Question 4: Scale our results and understanding of three focal lake systems to a diverse set of lake systems representative of continental-scale gradients
Models
Hydrological Modeling: Pennsylvania Integrated Hydrological Model (PIHM); Cycles (CropSyst)
- Leads: Chris Duffy, Armen Kemanian
Agricultural Economic Modeling: Stochastic Dynamic Programming (SDP)
- Lead: Kelly Cobourn
Limnological Modeling: General Lake Model (GLM)
- Leads: Cayelan Carey, Paul Hanson
Economic Property Value Modeling: Hedonic Model
- Lead: Kevin Boyle
Collective Action Modeling: Social Science Model
- Lead: Michael Sorice
Scaling up and extrapolation: LAke multi-scaled GeOSpatial and temporal database (LAGOS)
- Leads: Cayelan Carey, Kelly Cobourn, Pat Soranno
Ongoing Science Activities
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Science Foundation.
MediaWiki Pointers
This site is built with the Organic Data Science framework, which is developed using the MediaWiki and Semantic MediaWiki platforms.
Here is a Quick Reference Guide for How to Use This Wiki Site.